Microsoft Excel is a handy software. We use Excel functions for our education, business, and financial analyses. Moreover, in light of the effective rate and the number of compounding periods per year calculating the nominal annual interest rate, we thoroughly use Excel NOMINAL function. With this in mind, we are going to learn how to use the NOMINAL function in Excel with an example.
Introduction to NOMINAL Function
The Excel Financial Functions section includes the NOMINAL Function. It determines the number of compounding periods per year and the nominal annual interest rate for a given effective interest rate. Alternatively, the NOMINAL function is the EFFECT function’s inverse calculation. The following equation describes their relation.
Where
- Nominal Rate = The nominal annual interest rate.
- Npery = The number of compound periods per year.
Therefore, NOMINAL determines the number of compounding periods per year and the nominal annual interest rate for a declared effective interest rate. When the effective rate and the number of compounding years are provided, the function will return the nominal yearly interest rate. In financial analysis, we frequently compare multiple bonds, therefore we’re curious to know which one offers the best overall return. Moreover, the NOMINAL function can be useful when comparing two bonds, one of which advertises a real interest rate and the other a nominal rate.
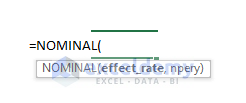
Syntax: The syntax of the NOMINAL function is as follows:
=NOMINAL(effect_rate, npery)Arguments Explanation:
| Arguments | Required or Optional | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| effect_rate | Required | A numeric value between 0 & 1 or a percentage. |
| npery | Required | The number of compound periods per year. |
Return Value: Returns the nominal annual interest rate.
How to Calculate Nominal Interest Rate Using NOMINAL Function: Practical Example
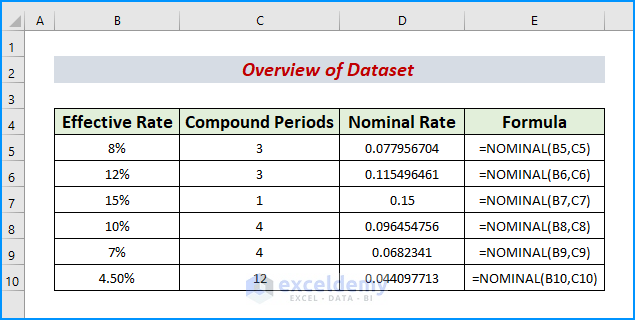
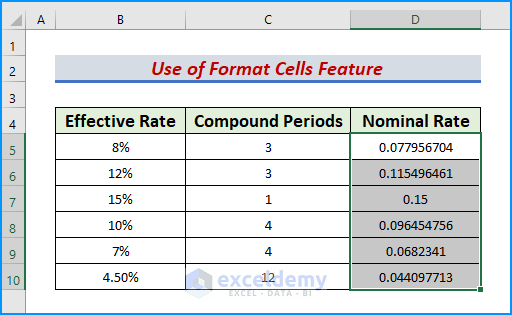
Calculating the annual nominal interest rates can be cumbersome if we have a large dataset. However, with the help of the NOMINAL function, we can determine them quickly and effectively. After we obtain the decimal values as outputs, we will format them in percentages using the Format Cells feature. Let’s get into it. To demonstrate, we take a dataset that represents annual nominal rates and periods of a credit bank.
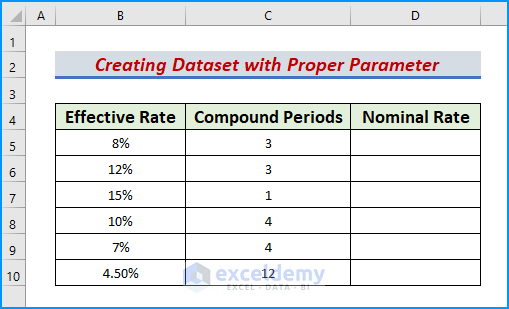
Step 1: Create Dataset with Proper Parameters
The first step aims to introduce a proper dataset with correct information. Let’s add the following sub-headings as follows.
- Include the headers Effective Rate, Compound Periods, and Nominal Rate in columns B, C, and D respectively.
- Afterward, populate the headers with the correct values.
- Thus, we obtain our desired dataset.
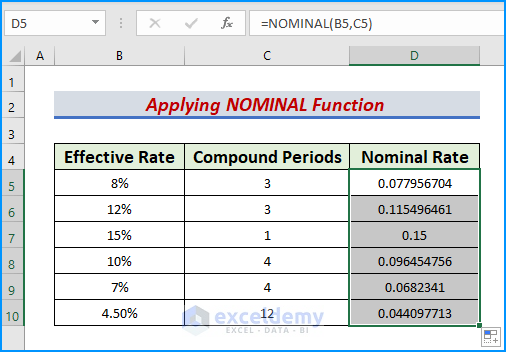
Step 2: Apply NOMINAL Function
The objective of the second step is to utilize the NOMINAL function for the given values. As already discussed, the function determines the nominal interest rate and returns a decimal. Therefore, let’s follow the instructions below to implement the function properly.
- First, type the following formula in cell D5,
=NOMINAL(B5,C5)- Later, press the Enter or Tab keys.
- As a result, we get an output in D5.
- Next, use the AutoFill tool to drag the output cell down.
- Hence, we obtain our desired nominal rates in our dataset.
- The Effective rate should be between 0 and 1.
- The Compound Periods have to be an Integer. If not, Excel will truncate the inputs.
Step 3: Use Format Cells Feature
In our last step, we will format the previously obtained decimal into percentages. To illustrate, we will use the Format Cells feature in Excel. To do so, follow the easy procedure below.
- First, select the range D5:D10 and right-click on the selected range.
- Consequently, a context menu pops up.
- There, locate the Format Cells option and tap on it.
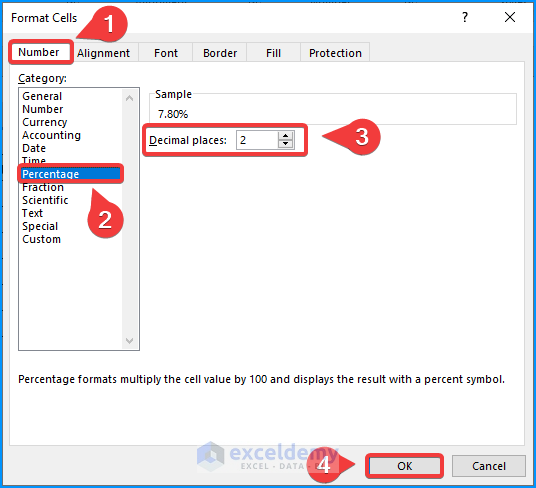
- Subsequently, the Format Cells dialog box appears.
- Further, go to Number → Percentage and then set the Decimal places to 2.
- Lastly, click OK to complete the formatting.
- Finally, we can see the effective rates in our display.
Reasons Behind NOMINAL Function Not Working in Excel
The common errors likely to appear are as follows.
- #NUM! appears if the given effective rate is ≤ 0.
- #NUM! also shows up if the given Npery is < 1.
- #VALUE! pops up if we input non-numeric values.
Download Practice Workbook
Download this workbook and practice while going through the article.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we have discussed some easy steps of how to use the NOMINAL function in Excel with an example. Please, leave any further queries or recommendations in the comment box below.
<< Go Back to Excel Functions | Learn Excel